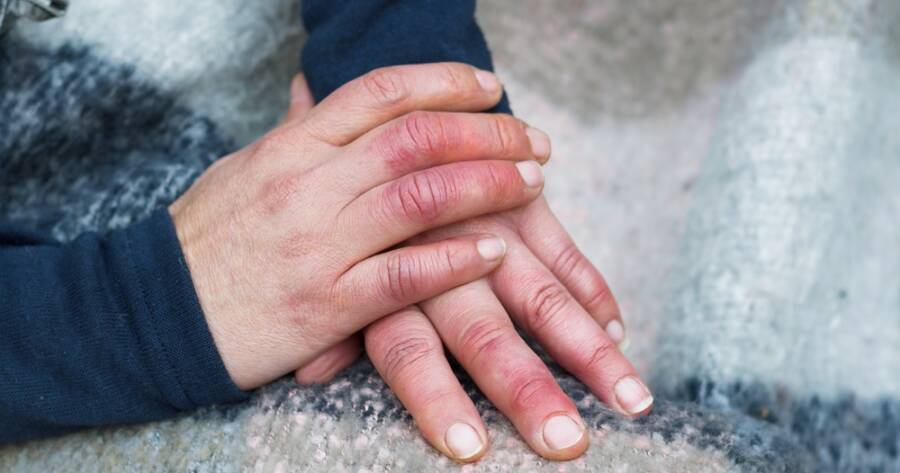
Raynaud’s disease, a condition affecting blood flow to certain parts of the body, can lead to discomfort and potential complications if not recognized early. Understanding the early warning signs is crucial for effective management and treatment. It often causes the fingers and toes to feel numb and cold in response to cold temperatures or stress. Identifying symptoms early might aid in minimizing discomfort and preventing progression. Understand the first signs of Raynaud’s disease and available treatments.
Recognizing the Early Signs
Raynaud’s disease manifests with distinct symptoms that primarily affect extremities such as fingers and toes. One of the earliest signs is a noticeable color change in response to cold or stress, where skin turns white or blue. This color shift results from reduced blood flow and oxygenation in affected areas.
Additionally, individuals experiencing Raynaud’s may notice numbness or tingling as blood vessels constrict. Once normal blood flow resumes, the skin may turn red, accompanied by a burning or throbbing sensation. These episodes can vary in duration and frequency. Awareness of these symptoms is invaluable for seeking timely medical consultation and confirming a diagnosis.
Understanding Triggers and Causes
Triggers for Raynaud’s disease often include exposure to cold weather, emotional stress, or vibrations from activities like typing or using tools. Understanding and avoiding these triggers can help individuals manage symptoms more effectively. It is also essential to differentiate between primary and secondary forms of Raynaud’s.
Primary Raynaud’s occurs independently without associated medical conditions and tends to be less severe. In contrast, secondary Raynaud’s is linked to other diseases such as scleroderma, lupus, or rheumatoid arthritis, often presenting more severe symptoms. Identifying the form of Raynaud’s is crucial for tailoring appropriate treatments and preventive measures.
Diagnostic Approaches
Proper diagnosis is essential for effectively managing Raynaud’s disease. Healthcare providers typically begin with a comprehensive medical history and physical examination, focusing on symptom patterns and possible underlying conditions. Nailfold capillaroscopy, a test examining small blood vessels near fingernails, can be used to detect abnormalities indicative of secondary Raynaud’s.
Blood tests might also be conducted to check for autoimmune disorders or markers suggesting secondary causes. Collaborating with healthcare professionals ensures accurate diagnosis and differentiates between primary and secondary forms. This clarity allows for an informed treatment plan that addresses individual health considerations comprehensively.
Lifestyle and Home Management Strategies
For many individuals managing Raynaud’s, lifestyle modifications play a significant role in minimizing symptom episodes. Keeping hands and feet warm by wearing layers, gloves, and insulated footwear helps prevent cold-induced symptoms. Additionally, stress-reducing practices such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises could lower the frequency of episodes related to emotional factors.
It’s beneficial to avoid smoking and limit caffeine intake, as these can constrict blood vessels and exacerbate symptoms. Regular physical activity may improve circulation overall, potentially reducing symptom severity. Incorporating these adjustments into daily routines might significantly enhance quality of life and symptom management without medical intervention.
Medical Treatments and Interventions
When lifestyle changes are insufficient, medical treatments may be considered to manage Raynaud’s symptoms more effectively. Calcium channel blockers are commonly prescribed for their ability to relax blood vessels, enhancing blood flow to affected areas. These medications may reduce the frequency and intensity of episodes for many patients.
In more severe cases, other medications such as vasodilators, which open blood vessels, or alpha blockers that counteract norepinephrine’s effects might be recommended. For those with secondary Raynaud’s, treating the underlying condition often alleviates associated symptoms. Regular consultations with healthcare providers provide opportunities to review the effectiveness of prescribed treatments and adjust as necessary.
Exploring Alternative Therapies
Some individuals explore alternative therapies alongside conventional treatments to manage Raynaud’s disease. Acupuncture may be considered for its potential influence on blood flow and reducing stress-related triggers. Biofeedback, a technique teaching how to control physiological functions such as heart rate, might also aid in mitigating stress responses.
Herbal remedies or dietary supplements like ginkgo biloba or omega-3 fatty acids are sometimes pursued for their reputed circulatory benefits. However, patients should approach these options with caution and consult healthcare providers about potential interactions with prescribed medications. Collaborating with professionals ensures comprehensive care and informed decisions regarding additional therapies.
Addressing Severe Symptoms and Complications
Although rare, severe Raynaud’s episodes can lead to complications like ulcers or tissue damage due to prolonged blood flow restriction. Ensuring immediate medical attention in such scenarios is vital to prevent serious harm. In extreme cases unresponsive to medication, surgical options such as sympathectomy, which interrupts nerve signals causing vasospasm, might be explored.
Developing an action plan for severe episodes, including when to seek emergency care, empowers individuals to manage Raynaud’s confidently. Constant communication with healthcare providers allows for proactive management, minimizing complications and optimizing symptom control for a better quality of life.
Stay Informed and Empowered
Awareness of Raynaud’s disease’s early signs and potential treatments empowers individuals to manage symptoms effectively and enhance their quality of life. Through lifestyle adjustments, medical interventions, and potentially exploring alternative therapies, one can mitigate the impact of this condition.
Engaging with healthcare providers facilitates accurate diagnosis and ensures comprehensive care tailored to individual needs. By taking proactive steps to understand and manage Raynaud’s disease, individuals can navigate challenges and maintain daily activities with greater comfort and assurance.