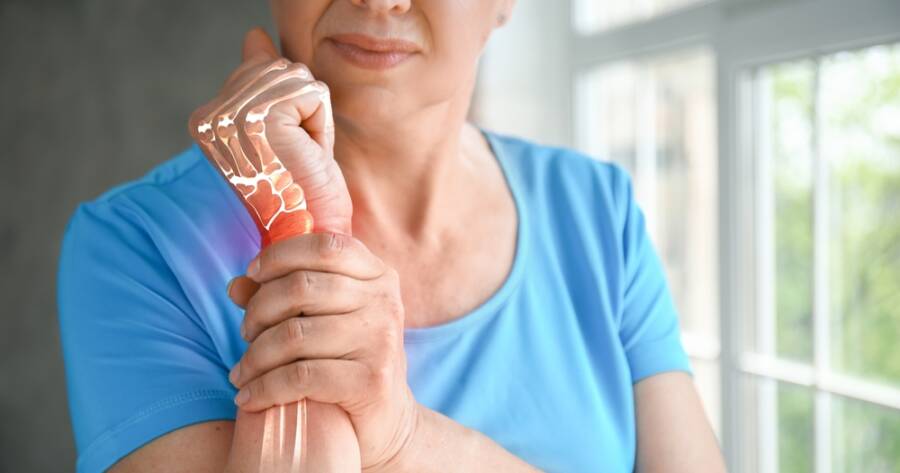
Arthrosis, a chronic condition characterized by the degeneration of joint cartilage, affects millions of people worldwide. While it’s often associated with aging, arthrosis can impact individuals of various ages due to factors such as genetics, injuries, or lifestyle habits. Recognizing the early signs of arthrosis is critical, as timely intervention can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. In this article, we’ll explore the common signs of arthrosis and why staying vigilant about them is essential for maintaining joint health.
What Is Arthrosis?
Arthrosis, also known as osteoarthritis, is a degenerative joint condition where the protective cartilage cushioning the ends of bones wears down over time. This condition can lead to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility in affected joints. While arthrosis is not curable, many approaches can potentially slow its progression, alleviate symptoms, and enhance daily function.
Arthrosis commonly affects weight-bearing joints such as the knees, hips, and spine, though it can occur in any joint. It’s essential to differentiate arthrosis from other joint-related conditions like arthritis, which involves inflammation. While arthrosis primarily results from wear and tear, inflammation may develop as the condition progresses, further complicating symptoms.
Early Signs of Arthrosis to Watch For
1. Joint Pain or Discomfort
One of the hallmark signs of arthrosis is persistent joint pain, which may initially appear after physical activity or at the end of the day. Pain can range from mild to severe, depending on the extent of cartilage damage. Some individuals report a dull ache, while others experience sharp, localized pain. If you notice recurring discomfort in specific joints, it’s worth discussing with a healthcare provider.
2. Morning Stiffness
Another early indicator of arthrosis is stiffness, particularly after waking up or remaining inactive for extended periods. While this stiffness often subsides within 30 minutes, it may become more prolonged or frequent as the condition advances. Morning stiffness may feel like a lack of flexibility or a tight sensation in the joints, making it challenging to perform routine tasks.
3. Decreased Range of Motion
Difficulty moving joints or performing activities that were once effortless can signal the onset of arthrosis. Reduced range of motion may manifest as trouble bending your knees, rotating your neck, or fully extending your fingers. Over time, this limitation can interfere with daily life, from climbing stairs to gripping objects.
4. Joint Clicking or Grinding (Crepitus)
A noticeable cracking, clicking, or grinding sound when moving a joint is known as crepitus. This can occur when the cartilage has thinned, causing bones to rub against each other. While occasional joint noises aren’t uncommon and aren’t always cause for concern, persistent or painful crepitus might warrant attention.
5. Swelling or Tenderness
Although arthrosis is primarily a degenerative condition, it can cause inflammation in response to joint damage. Swelling, tenderness, or warmth around the joint may develop, particularly after extended activity. This symptom is often subtle in the early stages but can become more pronounced as the condition progresses.
6. Bone Spurs or Hard Knots Around Joints
Bone spurs, or small bony growths, can form along the edges of joints affected by arthrosis. These growths may feel like hard lumps near the joint and can contribute to discomfort or restricted movement. In the fingers, for instance, these spurs may create noticeable changes in appearance, sometimes referred to as Heberden’s or Bouchard’s nodes.
Why Paying Attention to Symptoms Matters
Ignoring early signs of arthrosis can lead to a cascade of challenges over time. If left unchecked, arthrosis may result in worsening pain, reduced mobility, and diminished quality of life. Beyond physical effects, untreated joint issues can impact mental health, contributing to stress, anxiety, or depression related to chronic discomfort and limited activity.
Seeking medical guidance when symptoms arise allows for an accurate diagnosis and the development of a tailored management plan. Early interventions such as physical therapy, weight management, and lifestyle modifications can potentially slow arthrosis progression. In some cases, medications or assistive devices may be recommended to address pain and improve function.
Steps to Take If You Notice Symptoms
1. Consult a Healthcare Professional
If you suspect arthrosis, start by scheduling a visit with your primary care provider or a specialist like a rheumatologist or orthopedic doctor. They may recommend imaging tests or physical examinations to assess the extent of joint damage.
2. Adopt Joint-Friendly Habits
Maintaining a healthy weight, staying physically active, and incorporating low-impact exercises like swimming or yoga can support joint health. Avoid activities that place excessive stress on affected joints, and consider using ergonomic tools or supports if needed.
3. Explore Treatment Options
Depending on the severity of your symptoms, your healthcare provider may suggest over-the-counter pain relievers, prescription medications, or alternative therapies like acupuncture. In advanced cases, surgical options like joint replacement might be considered.
Conclusion
Arthrosis is a common yet often misunderstood condition that can significantly impact daily life if left unaddressed. Recognizing the early signs, such as joint pain, stiffness, or reduced mobility, is crucial for seeking timely support and developing strategies to manage the condition. While there’s no guarantee of preventing or reversing arthrosis, proactive care can empower individuals to maintain a more active and fulfilling lifestyle. If you’re experiencing symptoms, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional—early action can make a meaningful difference.